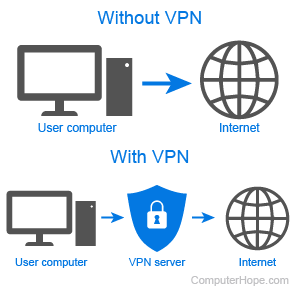
FortiClient VPN: Complete Guide to Secure Remote Access
Download and install FortiClient VPN for enterprise-grade security across all your devices. Free VPN client with SSL VPN and IPsec VPN support.
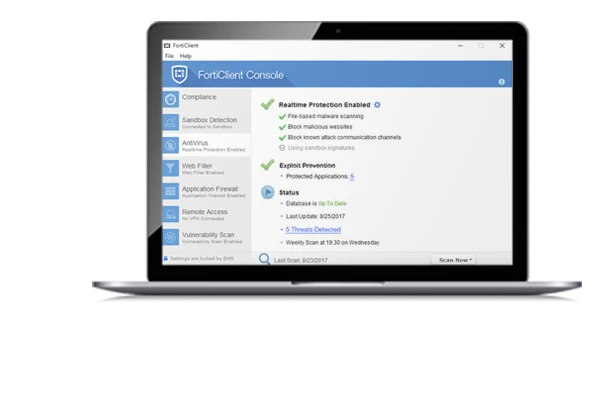
Why Choose FortiClient VPN?
Enterprise-Grade Security
FortiClient VPN delivers military-grade encryption and security protocols trusted by Fortune 500 companies worldwide. Protect your sensitive data with industry-leading SSL VPN and IPsec VPN technologies.
Multi-Platform Support
Access secure VPN connections from Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, and Android devices. FortiClient VPN ensures seamless protection across all your endpoints with consistent security policies.
High Performance
Experience fast and reliable VPN connections with optimized tunneling protocols. FortiClient VPN minimizes latency while maintaining maximum security for your remote work requirements.
Advanced Threat Protection
Integrated endpoint protection with real-time threat intelligence from FortiGuard Labs. Defend against malware, ransomware, and zero-day attacks while connected to the VPN.
Easy to Use
Intuitive interface designed for both IT professionals and end users. Quick setup, automatic connection, and simple configuration make FortiClient VPN accessible to everyone.
Centralized Management
IT administrators can deploy, configure, and monitor FortiClient VPN endpoints through FortiClient EMS. Streamline security policy enforcement across your organization.
What is FortiClient VPN?
FortiClient VPN is a comprehensive endpoint security solution developed by Fortinet, a global leader in cybersecurity. This powerful VPN client enables secure remote access to corporate networks, protecting data transmission with advanced encryption protocols. FortiClient VPN combines traditional VPN functionality with next-generation endpoint protection, creating a unified security fabric for modern enterprises.
The FortiClient VPN application supports both SSL VPN and IPsec VPN protocols, offering flexibility for different network environments and security requirements. Whether you're working from home, a coffee shop, or traveling internationally, FortiClient VPN ensures your connection remains private and secure from potential threats.
Key Features of FortiClient VPN
SSL VPN and IPsec VPN Support
FortiClient VPN offers comprehensive support for both SSL VPN (Secure Sockets Layer Virtual Private Network) and IPsec VPN (Internet Protocol Security Virtual Private Network) protocols. SSL VPN provides easy-to-use, browser-like connectivity that works through most firewalls and proxy servers, making it ideal for remote workers who need quick access to corporate resources. IPsec VPN, on the other hand, delivers robust site-to-site and client-to-site connectivity with strong encryption standards including AES-256.
The dual-protocol support ensures that organizations can choose the most appropriate VPN technology based on their specific requirements. SSL VPN excels in scenarios requiring application-level access and works seamlessly with web-based applications, while IPsec VPN provides superior performance for full network access and supports advanced routing protocols.
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
FortiClient VPN incorporates Zero Trust Network Access principles, moving beyond traditional perimeter-based security models. ZTNA validates user identity, device security posture, and application access rights before granting network connectivity. This approach significantly reduces the attack surface by ensuring that users only access the specific resources they need, rather than gaining broad network access.
The ZTNA functionality integrates with FortiClient's endpoint compliance checking, verifying that connecting devices meet security standards before allowing VPN access. This includes checking for updated antivirus signatures, operating system patches, and compliance with corporate security policies.
Endpoint Protection and Antivirus
Beyond VPN connectivity, FortiClient includes comprehensive endpoint protection features. The integrated antivirus engine, powered by FortiGuard Labs threat intelligence, provides real-time protection against malware, spyware, ransomware, and other malicious software. This multi-layered approach ensures that endpoints remain secure even when connected through the VPN tunnel.
The endpoint protection system includes web filtering capabilities that block access to malicious websites, phishing attempts, and inappropriate content. Application firewall rules can be configured to control which applications can access network resources, adding an additional security layer beyond traditional network firewalls.
Multi-Factor Authentication
FortiClient VPN supports various multi-factor authentication (MFA) methods to strengthen access security. Integration with FortiToken, SMS-based authentication, email tokens, and third-party authentication providers ensures that VPN access requires more than just a username and password. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access due to compromised credentials.
Organizations can configure authentication policies based on user groups, locations, and device types. For example, access from unknown devices or locations can require additional authentication factors, while trusted devices on secure networks may use streamlined authentication processes.
How to Use FortiClient VPN
Initial Setup and Configuration
Setting up FortiClient VPN is straightforward and user-friendly. After downloading and installing the appropriate version for your operating system, launch the FortiClient application. The initial configuration requires your organization's VPN gateway address, which your IT administrator will provide. This typically appears as a URL or IP address that serves as the connection endpoint.
Navigate to the "Remote Access" section within FortiClient and click "Configure VPN." Enter the connection name (for easy identification), the remote gateway address, and select either SSL VPN or IPsec VPN as your connection protocol. If your organization uses custom port numbers or specific authentication requirements, these settings can be configured in the advanced options.
For SSL VPN connections, you may need to specify whether you're connecting to a specific portal or tunnel group. Your administrator will provide these details if required. IPsec VPN connections require additional parameters such as authentication methods, phase 1 and phase 2 encryption settings, and pre-shared keys or certificate information.
Connecting to VPN
Once configured, connecting to the VPN is simple. Open FortiClient and select your configured VPN connection from the list. Click "Connect" and enter your credentials when prompted. Depending on your organization's security policies, you may need to complete additional authentication steps such as entering a token code or approving a push notification on your mobile device.
The connection process typically takes 5-15 seconds, depending on network conditions and authentication requirements. Once connected, FortiClient displays a "Connected" status with connection details including assigned IP address, connection duration, and data transfer statistics. A system tray icon also indicates your active VPN status, providing quick visual confirmation of your secure connection.
Advanced Configuration Options
FortiClient VPN offers numerous advanced configuration options for power users and IT administrators. Split tunneling allows you to route only specific traffic through the VPN while letting other traffic access the internet directly. This can improve performance for non-corporate applications while maintaining security for business resources.
Auto-connect features can be configured to automatically establish VPN connections when starting the application or when connecting to specific networks. This ensures continuous protection without requiring manual intervention. Connection rules can specify when FortiClient should connect, disconnect, or maintain always-on VPN connectivity based on network conditions and location.
FortiClient VPN for Different Operating Systems
FortiClient VPN for Windows
The Windows version of FortiClient VPN is the most feature-rich implementation, supporting all security capabilities including VPN, antivirus, web filtering, application firewall, and vulnerability scanning. Compatible with Windows 10, Windows 11, and Windows Server editions, the client integrates seamlessly with Windows security features and supports both 32-bit and 64-bit architectures, including ARM64 for newer Windows devices.
Windows users benefit from native integration with Windows Defender, group policy support for enterprise deployments, and MSI-based installation packages for automated deployment through software management systems. The Windows client also supports single sign-on (SSO) integration with Active Directory, simplifying authentication for corporate users.
FortiClient VPN for macOS
FortiClient VPN for macOS delivers comprehensive security for Apple computers, supporting both Intel and Apple Silicon (M1/M2) processors. The Mac client provides VPN connectivity, web filtering, and malware protection while adhering to Apple's security and privacy standards. Integration with macOS security features ensures smooth operation without compromising system performance.
Mac users appreciate the native macOS interface design and support for macOS-specific features like Touch ID authentication and Keychain integration for secure credential storage. The client supports all recent macOS versions and receives regular updates to maintain compatibility with new OS releases.
FortiClient VPN for Linux
Linux users can access FortiClient VPN through both GUI and command-line interfaces, making it suitable for desktop users and server administrators. The Linux client supports major distributions including Ubuntu, Debian, Red Hat Enterprise Linux, CentOS, and Fedora. Packages are available in DEB and RPM formats for easy installation on different Linux variants.
The command-line interface enables automation and scripting of VPN connections, making it ideal for DevOps workflows and automated deployment scenarios. System administrators can integrate FortiClient VPN into shell scripts, configuration management tools, and continuous integration pipelines.
FortiClient VPN Mobile Apps
Mobile versions of FortiClient VPN for iOS and Android enable secure remote access from smartphones and tablets. The mobile apps focus on VPN connectivity and essential security features optimized for mobile operating systems and battery life. Both versions support SSL VPN and IPsec VPN protocols with simplified configuration for mobile users.
The mobile clients include features like automatic VPN reconnection when switching between Wi-Fi and cellular networks, certificate-based authentication for enhanced security, and integration with mobile device management (MDM) solutions for enterprise deployment. Push notifications alert users to security events and connection status changes.
Security Best Practices with FortiClient VPN
Always Enable VPN on Untrusted Networks
When connecting to public Wi-Fi networks at airports, hotels, coffee shops, or other public venues, always activate your FortiClient VPN before accessing any corporate resources or sensitive data. Public networks are inherently insecure and susceptible to man-in-the-middle attacks, packet sniffing, and other security threats. The VPN encryption ensures that even if attackers intercept your traffic, they cannot decrypt or read your data.
Configure FortiClient's auto-connect feature to automatically establish VPN connections when joining untrusted networks. This eliminates the risk of forgetting to enable VPN protection and ensures continuous security regardless of your location.
Keep FortiClient Updated
Regular updates are crucial for maintaining optimal security with FortiClient VPN. Fortinet frequently releases updates that include security patches, bug fixes, new features, and updated threat signatures. Enable automatic updates within FortiClient settings to ensure you're always running the latest version with the most current protection capabilities.
Organizations should implement policies requiring all endpoints to run current FortiClient versions. FortiClient EMS can enforce version compliance and automatically deploy updates across managed endpoints, ensuring consistent security posture throughout the organization.
Use Strong Authentication
Implement multi-factor authentication for all FortiClient VPN connections. Combining passwords with additional authentication factors like hardware tokens, mobile authenticator apps, or biometric verification significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. Even if credentials are compromised through phishing or other attacks, the additional authentication factor prevents unauthorized VPN access.
Regularly rotate passwords and avoid reusing credentials across multiple systems. Consider implementing certificate-based authentication for an even stronger security posture, especially for privileged users and administrators.
Troubleshooting Common FortiClient VPN Issues
Connection Failures
If FortiClient VPN fails to establish a connection, first verify that you have active internet connectivity. Test by opening a web browser and accessing a known website. If internet access works but VPN doesn't connect, check that you've entered the correct gateway address and credentials. Verify with your IT administrator that your account has VPN access permissions.
Network firewalls or security software may block VPN protocols. SSL VPN typically uses TCP port 443 (same as HTTPS), while IPsec VPN uses UDP ports 500 and 4500. Ensure these ports aren't blocked by your local firewall, router, or ISP. Some corporate networks or countries may restrict VPN usage, requiring alternative connectivity methods.
Slow Performance
VPN connections add encryption overhead and routing distance, which can impact performance. If you experience slow speeds, try connecting to a different VPN gateway closer to your physical location. Configure split tunneling to route only corporate traffic through the VPN while allowing other internet traffic to bypass the tunnel, improving overall performance.
Check your local internet connection speed – VPN performance cannot exceed your base internet bandwidth. Close bandwidth-intensive applications, disable unnecessary background processes, and ensure no other users on your network are consuming excessive bandwidth. Consider upgrading your internet plan if VPN usage is a regular requirement.
Authentication Problems
Authentication failures often result from incorrect credentials, expired passwords, or time synchronization issues with token-based authentication. Verify that your username and password are correct and that your account hasn't been locked due to failed login attempts. If using time-based tokens, ensure your device clock is accurately synchronized with network time servers.
Certificate-based authentication issues may require verifying that client certificates are properly installed and haven't expired. Check certificate validity dates and ensure the certificate chain is complete with all intermediate and root certificates properly configured.
FortiClient VPN vs Other VPN Solutions
Enterprise Integration
Unlike consumer VPN services, FortiClient VPN is designed specifically for enterprise deployments with deep integration into Fortinet's Security Fabric. This integration enables coordinated security policies across firewalls, switches, access points, and endpoint devices. Organizations using Fortinet infrastructure benefit from seamless policy enforcement and centralized visibility across their entire network.
Consumer VPN services focus primarily on privacy and geo-location flexibility, while FortiClient VPN emphasizes security, compliance, and access control. The endpoint security features included with FortiClient provide comprehensive protection beyond simple VPN connectivity.
Compliance and Auditing
FortiClient VPN includes extensive logging and reporting capabilities required for compliance with regulations like HIPAA, PCI-DSS, GDPR, and SOX. Detailed connection logs, authentication events, and security posture information enable organizations to demonstrate compliance and respond to audit requirements. Integration with SIEM systems allows security teams to correlate VPN events with other security data for comprehensive threat detection.
Getting Started with FortiClient VPN
Ready to experience secure remote access with FortiClient VPN? Download the appropriate version for your device and follow the setup instructions provided by your IT administrator. If you're evaluating FortiClient VPN for your organization, contact Fortinet or an authorized partner for demo access and deployment guidance.
FortiClient VPN continues to evolve with new features, enhanced security capabilities, and improved performance. Whether you're a remote worker needing secure access to corporate resources or an IT administrator deploying enterprise-wide VPN solutions, FortiClient VPN delivers the security, reliability, and functionality required for modern remote work environments.
Ready to Secure Your Connection?
Download FortiClient VPN now and experience enterprise-grade security for all your devices.
Download VPN Now